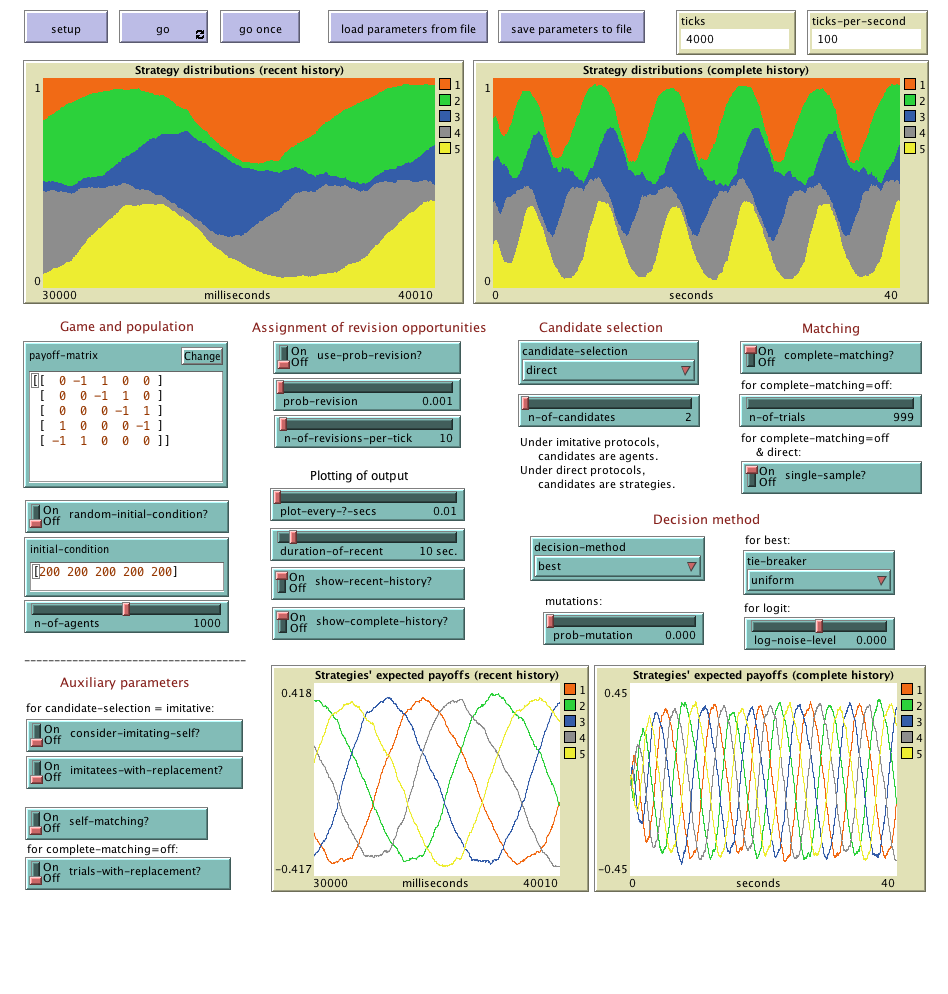
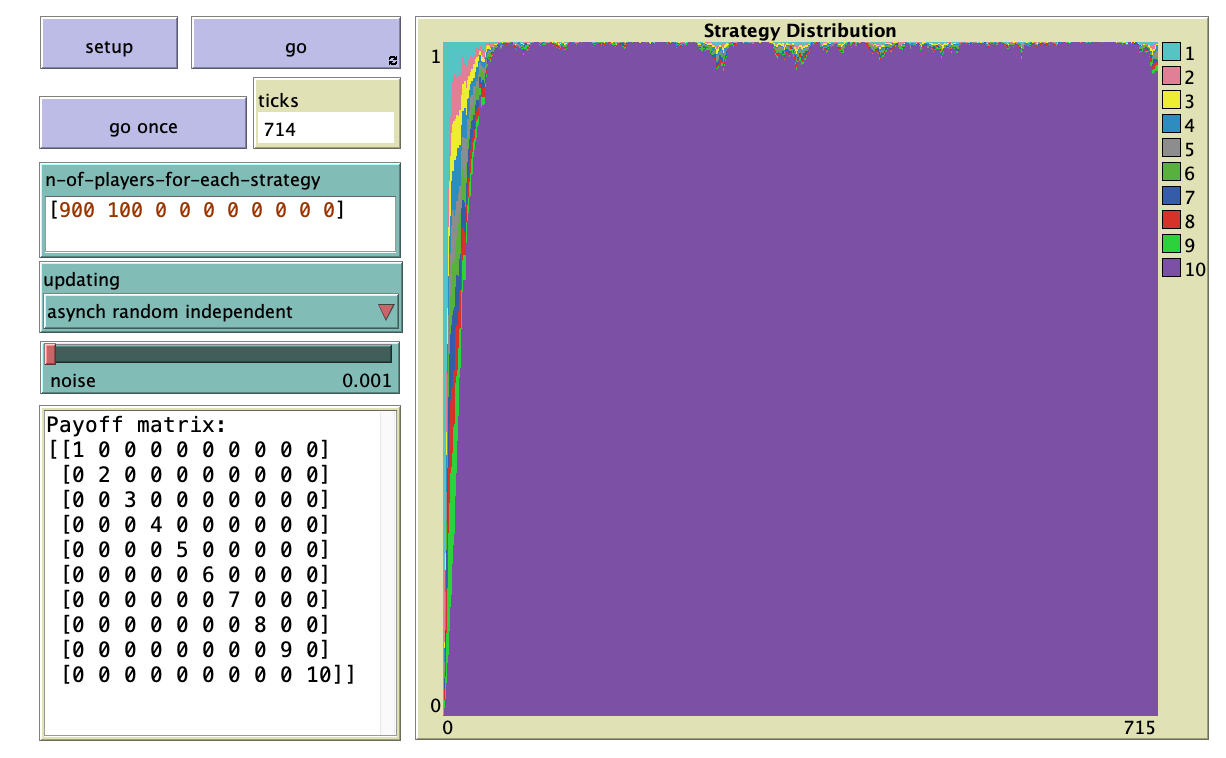
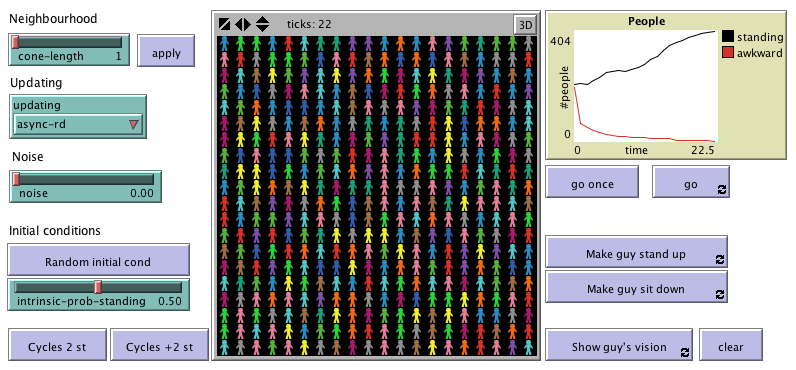
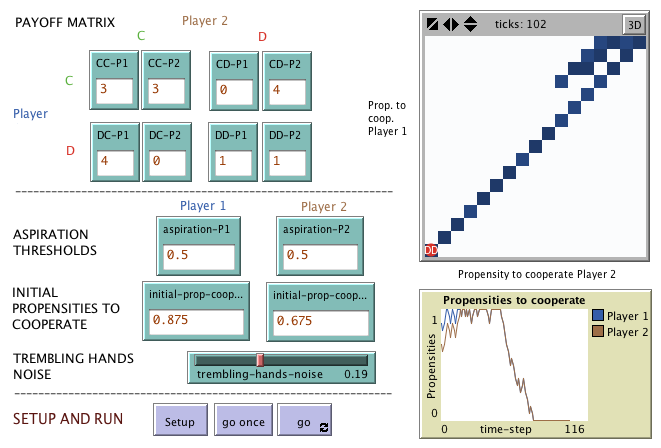
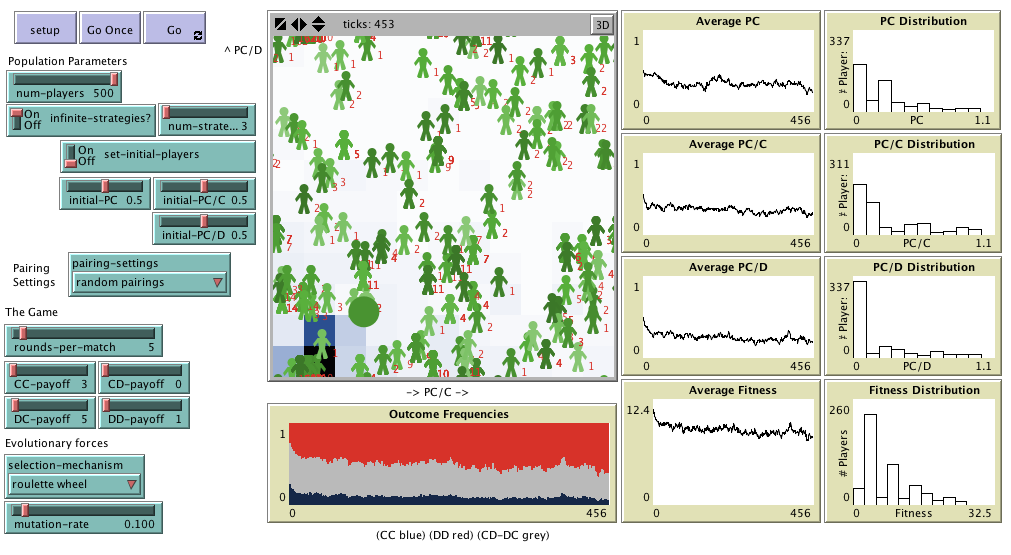
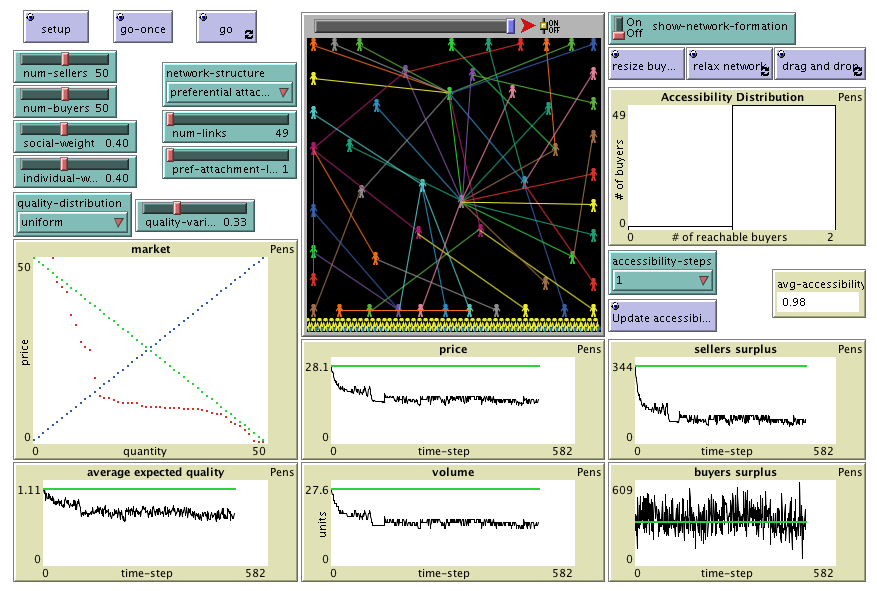
"Agent-Based Evolutionary Dynamics with 1 population" is
a modeling framework designed to simulate the evolution of a population of agents who play a
symmetric 2-player game and, from time to time, are given the opportunity to revise their strategy.
Explanatory paper:
"An Introduction to ABED: Agent-Based Simulation of Evolutionary Game Dynamics"
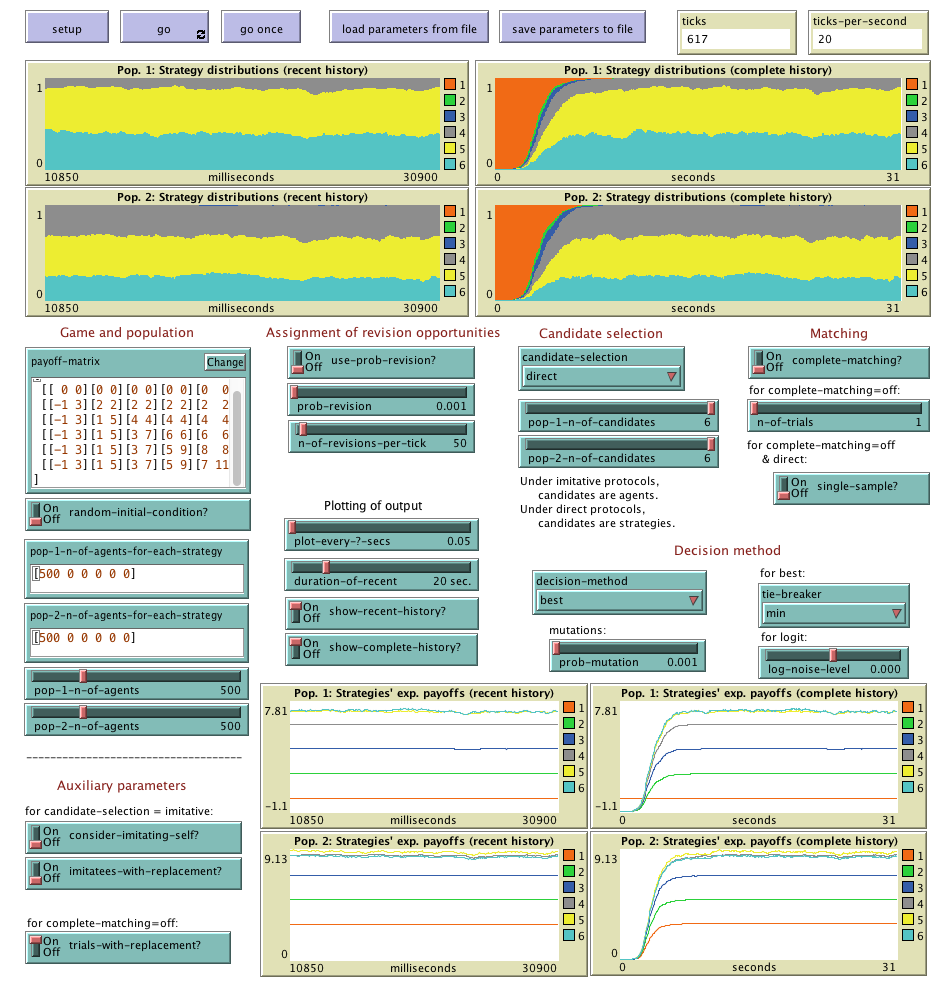
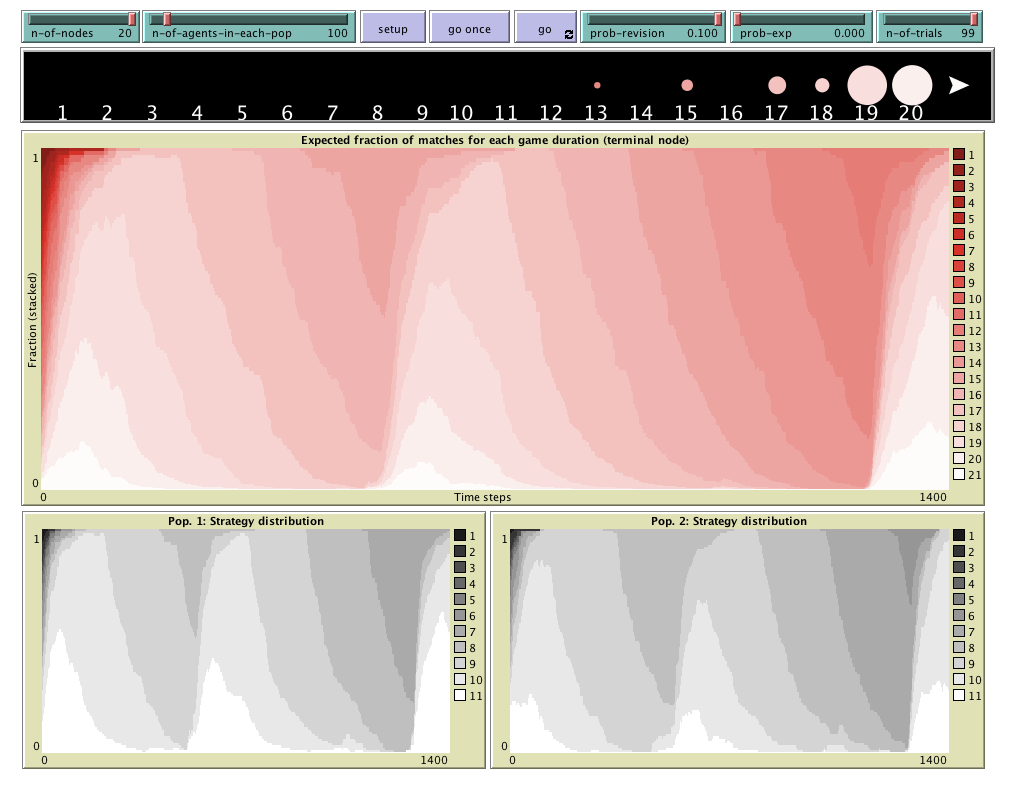
"Agent-Based Evolutionary Dynamics with 2 populations" is
a modeling framework designed to simulate the evolution of two populations of agents who play a
2-player game. Agents in one population play the game with agents in the other population. Every
agent is occasionally given the opportunity to revise his strategy. Explanatory paper:
"An Introduction to ABED: Agent-Based Simulation of Evolutionary Game Dynamics"
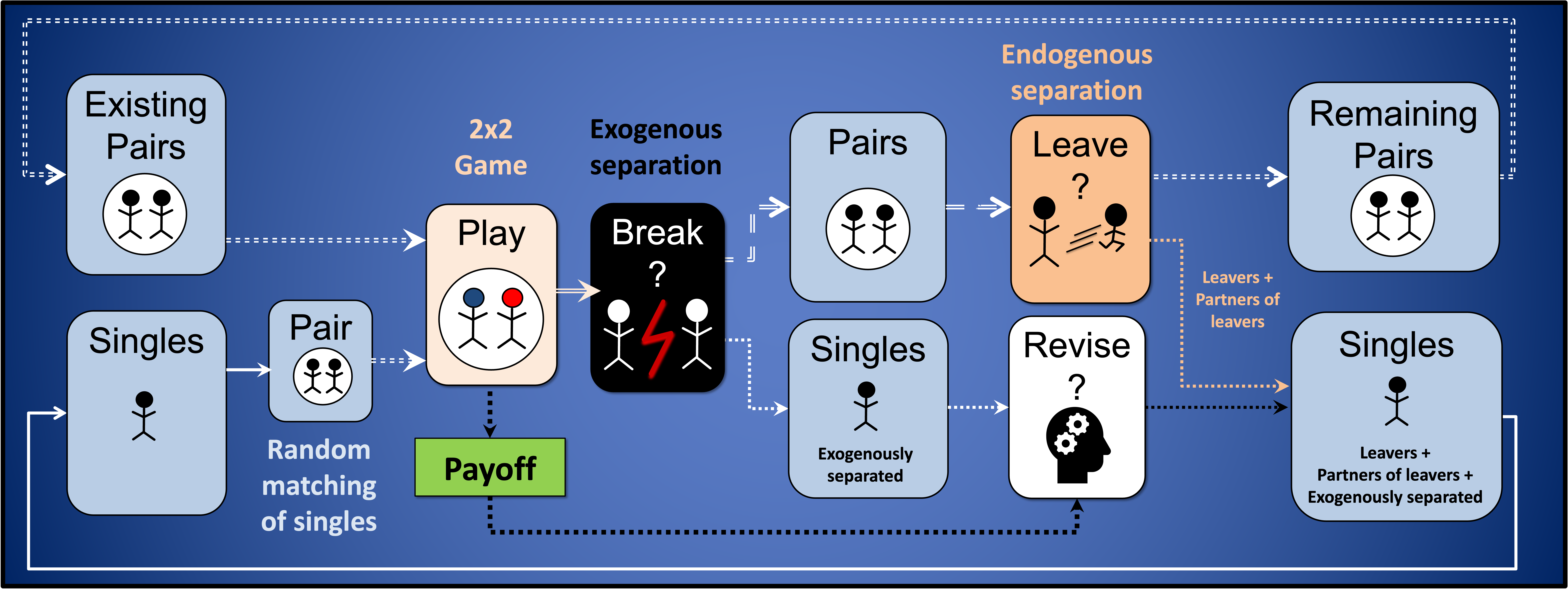
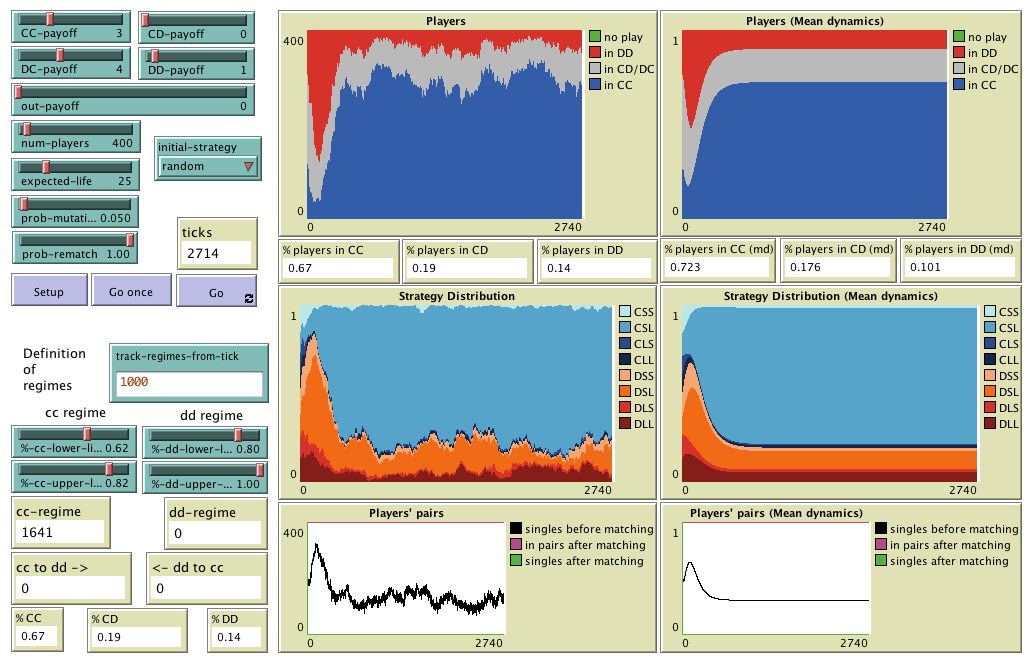
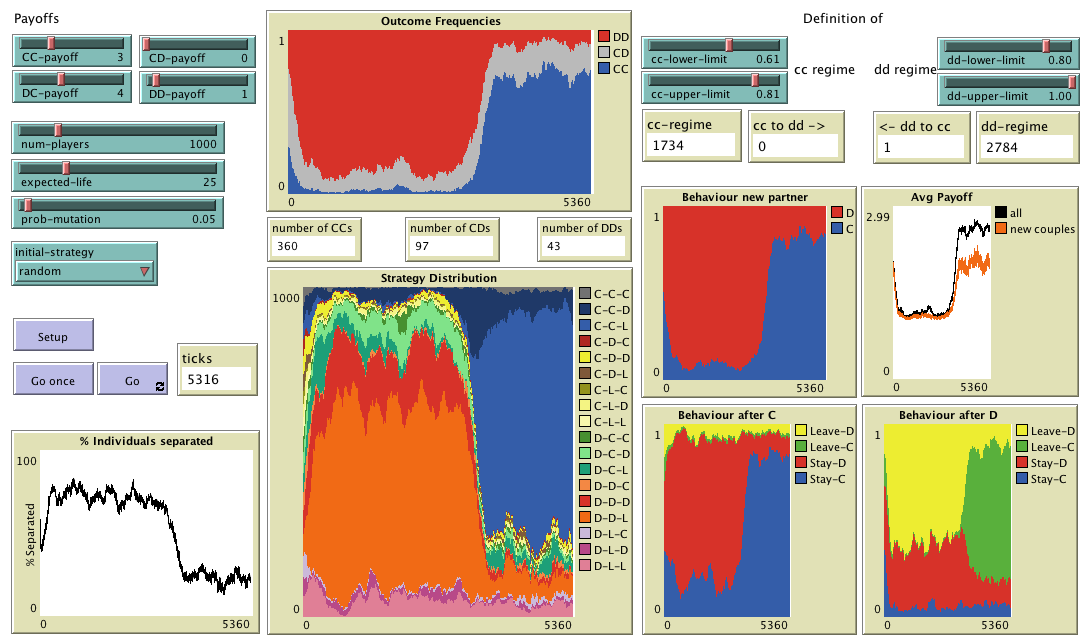
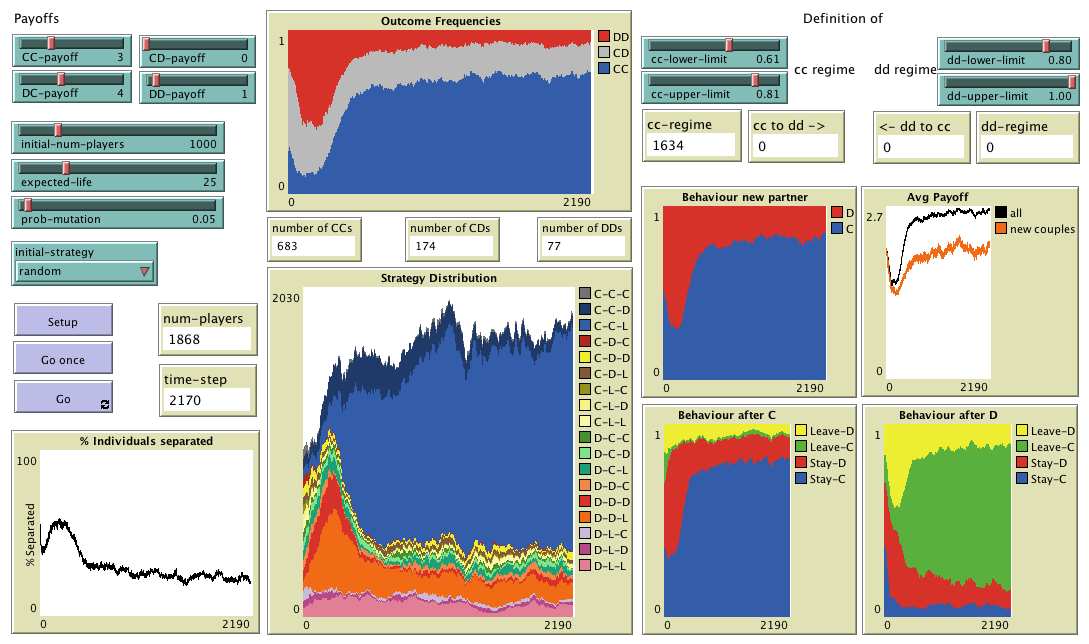
Agent-based model designed to analyse the effect of conditional dissociation in the evolutionary
emergence of cooperation. Included as supplementary material in the paper "Successful strategies in
the voluntarily repeated Prisoner’s Dilemma"
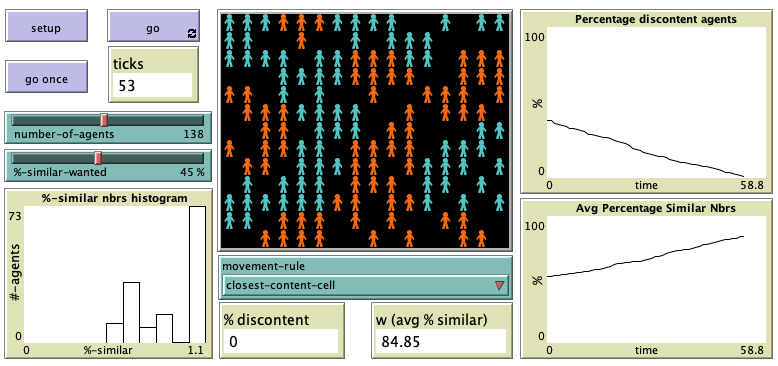
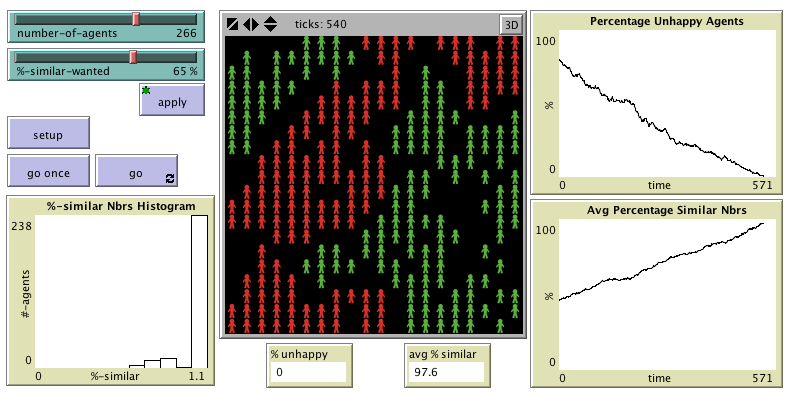
Schelling-Sakoda model of spatial segregation. Included in the paper
"Social simulation models as refuting machines"
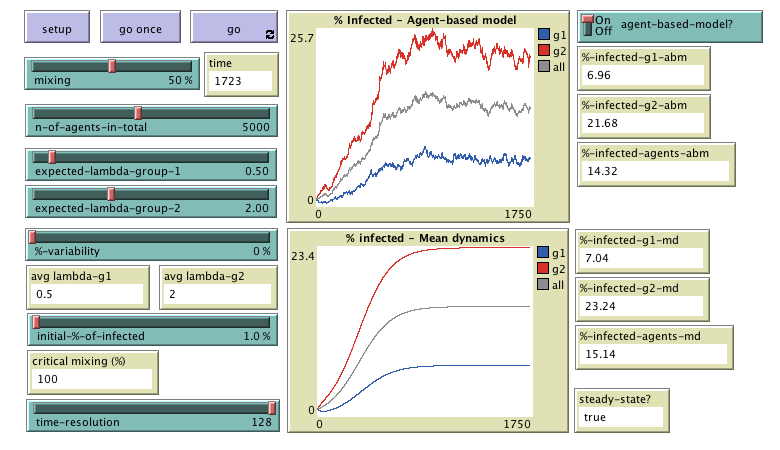
MiCoPro (Mixing in Contagion
Processes) is a model designed to analyze the consequences of mixing two groups
that have different predispositions to adopt a certain trait (or infection). Included as
supplementary material in the paper
"To mix or not to mix? Diffusion and segregation in heterogeneous groups"
Agent-based model (together with its mean-dynamics approximation running by its side) designed to
analyse the effect of conditional dissociation in the evolutionary emergence of cooperation, in the
simplest possible setting. Included as supplementary material in the paper
"Leave and let leave: A sufficient condition to explain the evolutionary emergence of
cooperation"
NetLogo model designed to analyze the nBEPA1 (noisy Best Experienced
Payoff, test All, 1 trial) protocol in Single Optimum
Coordination Games). Included as supplementary material in the paper
"Fast and Scalable Global Convergence in Single-Optimum Decentralized Coordination Problems"
Agent-based model designed to analyse the "Test two, choose the better" rule in the centipede game.
Included as supplementary material in the paper
"'Test two, choose the better' leads to high cooperation in the Centipede game"
NetLogo model designed to analyze the nBEPA1 (noisy Best Experienced
Payoff, test All, 1 trial) protocol in Single Optimum
Coordination Games played in networks. Included as supplementary
material in the paper
"Fast and Scalable Global Convergence in Single-Optimum Decentralized Coordination Problems"
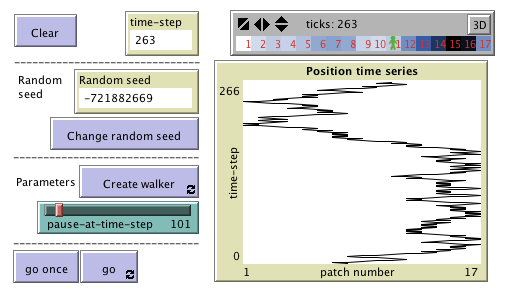
Simulation of a 1-dimensional random walk. Included in the paper
"Techniques to Understand Computer Simulations: Markov Chain Analysis"
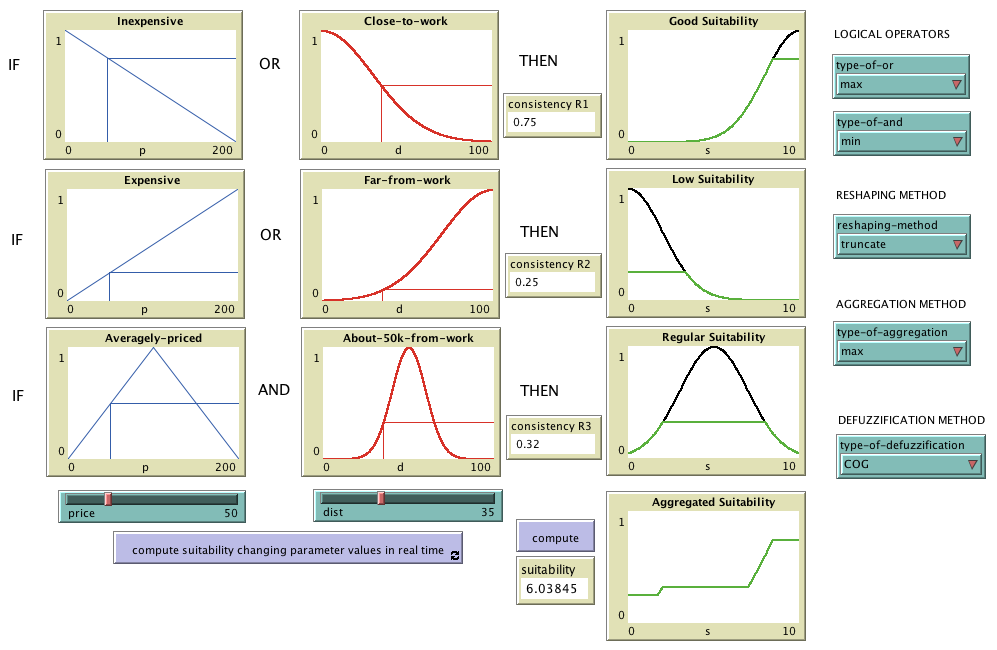
NetLogo extension that facilitates the use of fuzzy logic within NetLogo. For further details,
please read the paper
"Fuzzy Logic for Social Simulation using NetLogo"
Collection of functions designed to facilitate the use of fuzzy logic within NetLogo. For further
details, please read the paper
"Fuzzy Logic for Social Simulation using NetLogo"
Cyp+By (constant population)
Agent-based model designed to analyse the effect of conditional dissociation in the evolutionary
emergence of cooperation. Included as part of the supplementary material of the paper
"The Option to Leave: Conditional Dissociation in the Evolution of Cooperation"
Cyp-By_fluctPop (fluctuating population)
Agent-based model designed to analyse the effect of conditional dissociation in the evolutionary
emergence of cooperation. Included as part of the supplementary material of the paper
"The Option to Leave: Conditional Dissociation in the Evolution of Cooperation"
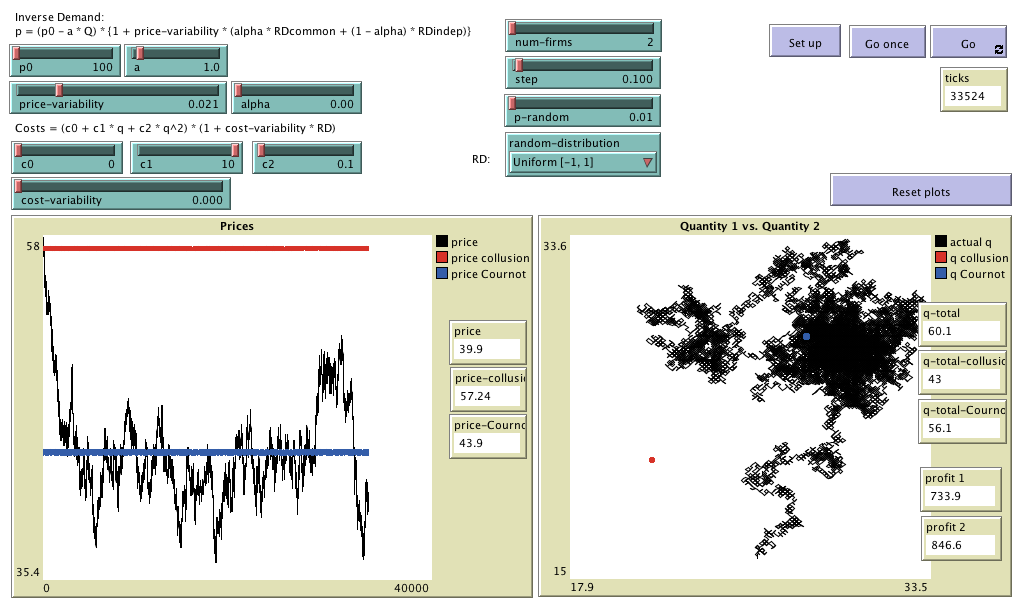
Model designed to analyse the Win-Continue, Lose-Reverse (WC-LR) rule in Cournot oligopolies. The
WC-LR decision rule considered here can be simply stated as: repeat your last action (i.e. an
increase or a decrease in production) if your profits have grown; otherwise, choose the opposite
action. Included as supplementary material in the paper
"The "Win-Continue, Lose-Reverse" Rule in Oligopolies: Robustness of Collusive Outcomes"
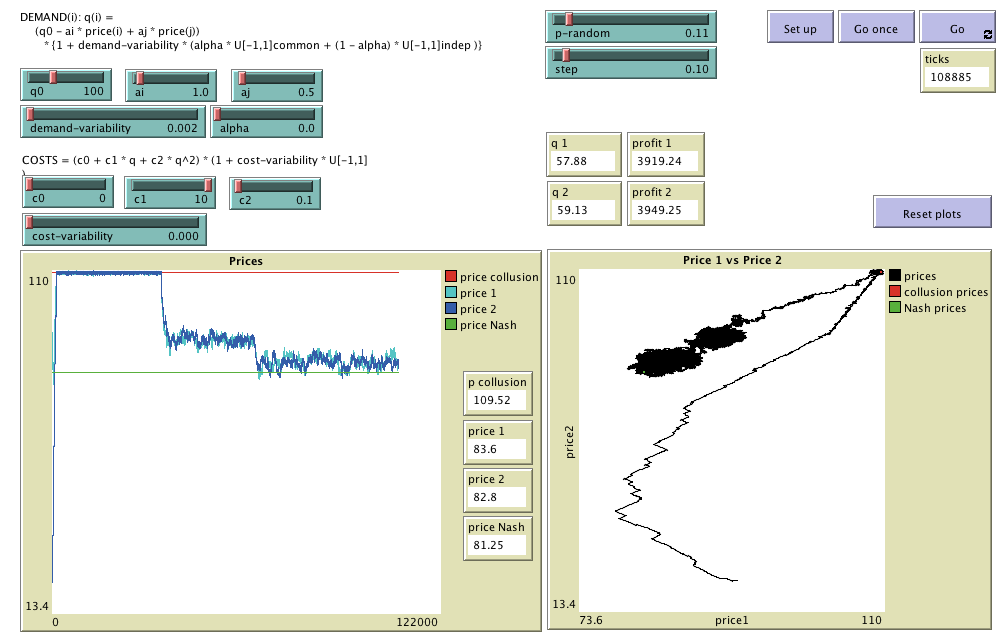
Model designed to analyse the Win-Continue, Lose-Reverse (WC-LR) rule in duopolies with
differentiated products where firms compete in prices. The WC-LR decision rule considered here can
be simply stated as: repeat your last action (i.e. an increase or a decrease in price) if your
profits have grown; otherwise, choose the opposite action. Included as supplementary material in
the paper
"The "Win-Continue, Lose-Reverse" Rule in Oligopolies: Robustness of Collusive Outcomes"
Agent-based model designed to illustrate how a deterministic approximation of a stochastic process
can be usefully applied to analyse the dynamics of many simple simulation models. Included in the
paper
"Stochastic Approximation to Understand Simple Simulation Models"
Agent-based model designed to illustrate the usefulness of the theory of Markov chains to analyse
computer models. Included as Appendix A in the paper
"Techniques to Understand Computer Simulations: Markov Chain Analysis"
Included in the Appendix B of the paper
"Techniques to Understand Computer Simulations: Markov Chain Analysis"
Included in the Appendix B of the paper
"Techniques to Understand Computer Simulations: Markov Chain Analysis"
Agent-based model where two reinforcement learners play a 2-player 2-strategy (2x2) game. Included
in the paper
"Techniques to Understand Computer Simulations: Markov Chain Analysis"
Modelling framework designed to formally investigate the evolution of strategies in 2-player
2-strategy (2x2) symmetric games under various competing assumptions. For more details, see paper
"On the structural robustness of evolutionary models of cooperation"
MEQU is an agent-based model designed to study the effects of quality uncertainty and incomplete
information on market dynamics. This model can be used to replicate every experiment reported in
the paper
"The impact of quality uncertainty without asymmetric information on market efficiency"
CharityWorld-JASSS is an agent-based model designed to show the emergent effects of floating-point
errors in agent-based models. This is done by showing how the model behaves dramatically
differently using floating-point arithmetic and using real arithmetic. This model was included as
Appendix B in the paper
"Is your model susceptible to floating-point errors?"
Recombranch is an evolutionary model of technological transitions designed to explore the
dynamics of innovation. The model is based on two different types of innovations: Branching
innovations and recombinant innovations. This model can be used to replicate every experiment
reported in the paper
"Branching innovation, recombinant innovation, and endogenous technological transitions"
This model can be used to replicate every experiment reported in the paper
"The economics of utopia: A co-evolutionary model of ideas, citizenship and socio-political
change"
InCaLead (Innovation, Catch-up and Leadership in Science-Based Industries) is
an evolutionary model designed to explore the role of scientists' mobility, and the interactions
among innovation, mobility and demand as key drivers of industrial leadership and catch-up. This
model can be used to replicate every experiment reported in the paper
"Innovation, Catch-up and Leadership in Science-Based Industries"
InDyTeRRoD (Industrial Dynamics and Technological Regimes and the
Role of Demand) is an evolutionary model designed to explore industrial
dynamics in alternative technological regimes. The model incorporates entry/exit mechanisms,
innovation, imitation, competition, strategic learning and firm growth in an innovative industry.
This model can be used to replicate every experiment reported in the paper
"Industry dynamics, technological regimes and the role of demand"